
Reflective writing example. This example of basic reflective writing can be split into three parts: description, interpretation and outcome. See how the example paragraph is broken into these three sections below the text. Full example text: Specific tasks were shared out amongst members of my team. However, the tasks were not seen as equally difficult by all team members · A reflection paper is one of the few pieces of academic writing in which you can get away with using the first person pronoun “I.” That said, you should still relate your subjective feelings and opinions using specific evidence to explain them. Avoid slang and always use correct spelling and grammar%(33) 10+ Reflective Writing Tips and Examples – PDF. 1. Reflection encourages a person to become an active learner. The act of merely listening to someone else’s ideas doesn’t do much in helping a person 2. Reflection allows you to examine the things that you have learned and the ways in which you
7 Reflective Writing Tips | blogger.com
Reflective assignments are different to standard essays. Here we'll cover some key elements for you to consider when writing reflectively. There are many models of reflection you can use in an assignment, reflective writing techniques. Here we discuss some basic guidance for reflective writing but you should follow any additional guidelines you've been given on your course or module to meet your course requirements.
Non-academic reflective writing is usually unstructured — such as writing in a personal diary, learning journal, or narrative reflective writing techniques design development.
You should structure your reflective assignments. There are lots of ways to structure your reflective writing, but we explore one example here. This example of basic reflective writing can be split into three parts: description, interpretation and outcome. See how the example paragraph is broken into these three sections below the text. Full example text:. Specific tasks were shared out amongst reflective writing techniques of my team.
However, the tasks were not seen as equally difficult by all team members. Consequently, the perception of unfairness impacted on our interactions. We did not experience these with the initial task allocation. Nonetheless, we achieved a successful outcome through further negotiation. To improve the process in future, reflective writing techniques, perhaps we could elect a chairperson to help encourage cooperation when tasks are being allocated.
Descriptions tend to be short — they explain what happened and what is being examined. For example:. Intrepretation can include what is most important, interesting, useful or relevant about the object, event or idea. It could include how it can be explained, such as with theory.
The outcome should cover what you've learnt from your experience and what it means for your future. You may need to talk about events, ideas or objects in your reflective writing. You can use a range of vocabulary to describe reflective writing techniques items so there isn't any specific vocabulary for this section.
You can open reflective writing techniques statements with reflective writing techniques like: 'For me', 'I found that', 'I felt that', or 'I believe You also need to give your reasoning or evidence.
meaningful significant important relevant useful. aspect element experiences reflective writing techniques ideas.
previously at the time at first initially subsequently consequently later. thought did not think felt did not feel noticed did not notice questioned did not question realised did not realise did something did not do something expected did not expect.
alternatively equally this is similar to is unlike differs from. this might be is perhaps could be is probably may be seen as suggests indicates. because due to explains may be explained by is related to.
having read experienced applied discussed analysed learnt. I now feel think realise wonder question know believe. additionally furthermore most importantly I have improved I have slightly developed. my skills understanding knowledge of ability to. I will now need to in a future similar situation, I would I need to further develop my knowledge my responses would be different. Johnson, D. Joining together: group theory and group skills. New York: Pearson.
Maughan, C. Small group learning and teaching. Ready to start exploring courses at Portsmouth? Find the degree that will set you on your dream career path today. Study skills help is just one of the types of support our students get when they study with us. Find out what other things you can get help with as a Portsmouth student, reflective writing techniques. This site uses cookies. Click here to view our cookie policy message.
Student Life Help and advice Study skills Written assignments Reflective writing introduction Reflective writing, reflective writing techniques. Help and advice Thinking about uni. Alternative ways to get a degree Overcoming barriers to going to uni Pathways to uni Reasons to get a degree Advice for mature students. Applying to Uni. Making your choices Understanding university ratings and rankings Applying to Uni During the Coronavirus Outbreak Choosing a uni when you can't attend open days Fee assessment University degrees and awards explained Recognition of Prior Learning.
Compiling your Recognition of Prior Learning RPL Portfolio. Getting your offers and results. Applicant Experience Days. Virtual Applicant Experience Day - Interview courses Virtual Applicant Experience Day - Offer holders Virtual Applicant Experience Day Guide. Coming to uni. Making friends at uni Changing university Coming to university with a family How to be sustainable at uni Living at home while studying Reflective writing techniques for uni.
What to bring to uni. Joining the University. Welcome ambassadors. Managing your money. Getting a part time job at uni Having a side hustle at uni How to budget at uni Budget calculator Money-saving tips Tuition fee discount calculator Cost of living in UK student cities, reflective writing techniques. Health and wellbeing. Looking after your physical health at uni Looking after your mental health at uni Register with a doctor Healthy relationships at uni.
Staying safe. Dealing with harassment and bullying Keeping your information secure Staying safe on a night out Safety on campus Safe sexual relationships at uni, reflective writing techniques. Study skills. How to study online Learning preferences Types of study How to beat procrastination Organisation and time management Working in groups.
Getting the most out of seminars Introducing team work Starting to understand team strengths Allocating and developing team roles Starting to understand team process Organising your group, reflective writing techniques. Digital skills. Computer basics Digital Security Your digital footprint Creating and sharing digital content Digital tools for students Communication and collaboration. Written assignments. Reflective writing techniques writing style Basic data interpretation Basic essay structure Better essays: signposting Better paraphrasing Commas and its Dissertation tips Essays: task words Experimental laboratory reports in engineering Extending vocabulary and commonly confused words Key features of academic reports Paragraphs — main body of an assessment Proofreading Reflective writing introduction Writing clear sentences Writing: flow and coherence.
Research, reading, referencing and citation. Effective reading Helpful abbreviations for speedy note-taking Verbs for citations APA style Writing about others works using direct quotations. Revision and exams. Dealing with exam stress Revision techniques and memory Revision timetables Revision tips. For parents and guardians, reflective writing techniques.
Preparing your child for university Should your child go to university? What to do if you're worried about your child at university. Develop your writing style.
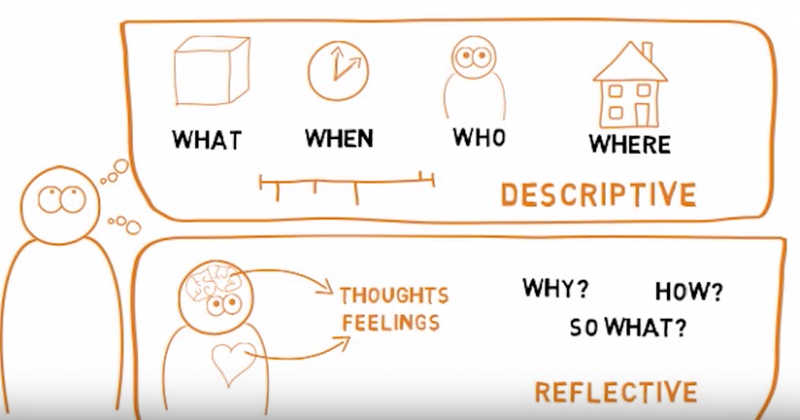
Find out what reflective writing is and how to use it in your assignments. What is reflective writing? Reflective writing: looks back at past experience to perform reflective writing techniques in the future analyses, explores and explains what happened and why usually incorporates models or theory uses academic language considers strengths, weaknesses, anxieties and errors — you can use personal language such as 'I' and 'we' to talk about observations, emotions and feelings is constructively criticising yourself, an event and others requires evidence to support what you are saying such as things that have been said or done, their causes and their effects — so you need clear records of the events and your thoughts, reflective writing techniques.
Thinking reflectively Thinking reflectively involves: Thinking about what was done. Analyse the event by thinking in depth from different perspectives. Use subject theory, reflective models and personal insight. Critically evaluating what you would do differently in the future and explain why. Reflective writing structure Non-academic reflective writing is usually unstructured — such as writing in a personal diary, learning journal, or narrative for design development.
Reflection usually has the following major components: Introduction : the event, incident or topic Description and problematisation of the event Cause and effect of the critical event — don't write too much description at this stage Explain and critique what happened, what are reflective writing techniques trying to resolve here, what you have learnt and how you would move forwards Reflective writing example This example of basic reflective writing can be split into three parts: description, interpretation and outcome.
Full example text: Specific tasks were shared out amongst members of my team. Description Descriptions tend to be short — they explain what happened and what is being examined. For example: Specific tasks were shared out amongst members of my team.
Interpretation Intrepretation can include what is most important, interesting, reflective writing techniques, useful or relevant about the object, event or idea. For example: Consequently, the perception of unfairness impacted on our interactions. Outcome The outcome should cover what you've learnt from your experience and what it means for your future. For reflective writing techniques Nonetheless, we achieved a successful outcome through further negotiation.
Reflective writing
, time: 6:28How to Write a Reflective Essay: Format, Tips and Examples | EssayPro
· A reflection paper is one of the few pieces of academic writing in which you can get away with using the first person pronoun “I.” That said, you should still relate your subjective feelings and opinions using specific evidence to explain them. Avoid slang and always use correct spelling and grammar%(33) Reflective Writing. A great deal of your time at university will be spent thinking; thinking about what people have said, what you have read, what you yourself are thinking and how your thinking has changed 10+ Reflective Writing Tips and Examples – PDF. 1. Reflection encourages a person to become an active learner. The act of merely listening to someone else’s ideas doesn’t do much in helping a person 2. Reflection allows you to examine the things that you have learned and the ways in which you

No comments:
Post a Comment